Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Res Vestib Sci > Volume 17(3); 2018 > Article
-
Case Report
외전신경마비가 동반된 Ramsay-Hunt 증후군 -
라혜주, 박재한

- Abducens Nerve Palsy Associated with Ramsay-Hunt Syndrome
-
Hye Joo Rha, Jae Han Park

-
Research in Vestibular Science 2018;17(3):116-118.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21790/rvs.2018.17.3.116
Published online: September 18, 2018
Department of Neurology, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- Corresponding Author: Jae Han Park Department of Neurology, Catholic University of Daegu, School of Medicine, Daegu Catholic University Hospital, 33 Duryugongwon-ro 17-gil, Nam-gu, Daegu 42472, Korea Tel: +82-53-650-3626 Fax: +82-53-654-9786 E-mail: jaehanpark@cu.ac.kr
• Received: July 26, 2018 • Revised: August 17, 2018 • Accepted: August 18, 2018
Copyright © 2018 by The Korean Balance Society. All rights reserved.
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 5,533 Views
- 164 Download
Abstract
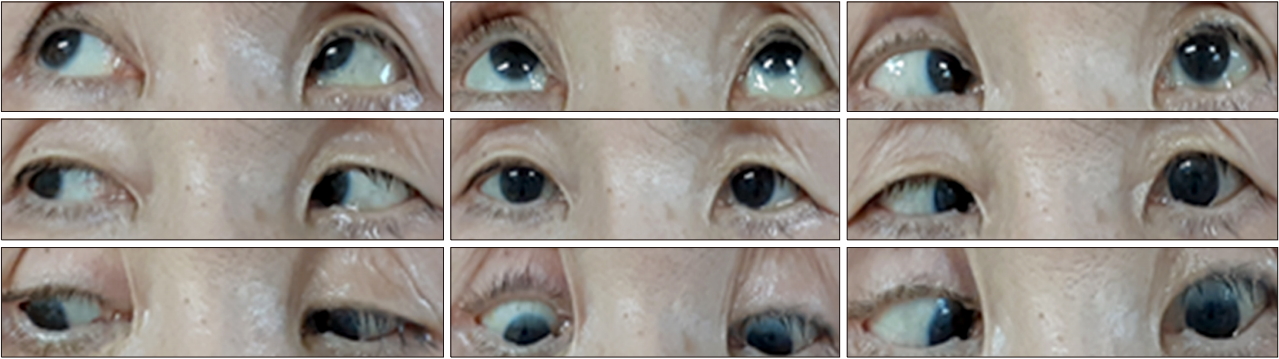
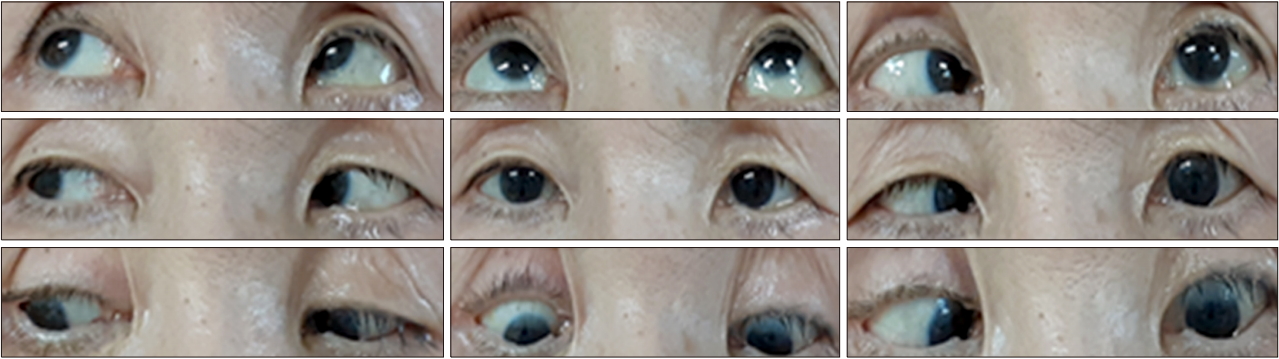
- Ramsay-Hunt syndrome is an infectious disease caused by the varicella zoster virus. It is usually associated with facial and vestibulocochlear nerve palsy, but other cranial nerve dysfunction can be accompanied. We present a 68-year-old woman with abducens nerve palsy associated with Ramsay-Hunt syndrome. She showed abduction limitation of left eye with peripheral facial palsy and vestibulopathy of the left side. Varicella zoster virus polymerase chain reaction of cerebrospinal fluid was positive and internal auditory canal magnetic resonance imaging was revealed enhancement of labyrinthine segment of left facial nerve. Although abducens nerve palsy is uncommon feature of Ramsay-Hunt syndrome, but it can be developed by several different mechanisms.
서 론
증 례
고 찰
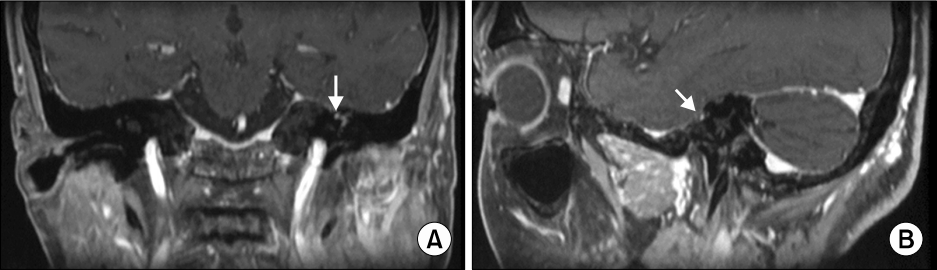
Fig. 2.Internal auditory canal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed partial inflammation of left facial nerve genu and labyrinthine segment (arrow). Coronal view (A) and sagittal view (B) of enhancement MRI.

- 1. Sweeney CJ, Gilden DH. Ramsay Hunt syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2001;71:149–54.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 2. Kim YH, Chang MY, Jung HH, Park YS, Lee SH, Lee JH, et al. Prognosis of Ramsay Hunt syndrome presenting as cranial polyneuropathy. Laryngoscope 2010;120:2270–6.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Shim HJ, Jung H, Park DC, Lee JH, Yeo SG. Ramsay Hunt syndrome with multicranial nerve involvement. Acta Otolaryngol 2011;131:210–5.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Hunt JR. The symptom-complex of the acute posterior poliomyelitis of the geniculate, auditory, glossopharyngeal and pneumogastric ganglia. Arch Intern Med (Chic) 1910;5:631–75.Article
- 5. Espay AJ, Bull RL. Petrositis in Ramsay Hunt syndrome with multiple cranial neuropathies. Arch Neurol 2005;62:1774–5.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Lapresle J, Lasjaunias P. Cranial nerve ischaemic arterial syndromes. A review. Brain 1986;109(Pt 1):207–16.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 7. Kim YH, Choi IJ, Kim HM, Ban JH, Cho CH, Ahn JH. Bilateral simultaneous facial nerve palsy: clinical analysis in seven cases. Otol Neurotol 2008;29:397–400.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Kim CH, Kang SI, Kim YH. A case of ramsay hunt syndrome with cranial polyneuropathy. Korean J Audiol 2012;16:80–2.ArticlePubMedPMC
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 


 KBS
KBS
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite