Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Res Vestib Sci > Volume 17(4); 2018 > Article
-
Case Report
경막외 신경차단술 시행 중 발생한 감각신경성난청과 어지럼 1예 -
이병민1, 노진홍2, 안성기1, 박현우1

- A Case of Sensorineural Hearing Loss and Vertigo during Epidural Nerve Block
-
Byeong Min Lee1, Jin hong Noh2, Seong Ki Ahn1, Hyun Woo Park1

-
Research in Vestibular Science 2018;17(4):170-174.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21790/rvs.2018.17.4.170
Published online: December 21, 2018
1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Korea
2Department of Neurology, New Tongyoung Hospital, Tongyoung, Korea
- Corresponding Author: Hyun Woo Park Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, 79 Gangnam-ro, Jinju 52727, Korea Tel: +82-55-750-8178 Fax: +82-55-759-0613 E-mail: phw83@hanmail.net
• Received: October 11, 2018 • Revised: December 3, 2018 • Accepted: December 4, 2018
Copyright © 2018 by The Korean Balance Society. All rights reserved.
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 4,622 Views
- 78 Download
Abstract
- Epidural anesthesia has significantly advanced in neuraxial anesthesia and analgesia. It is used for surgical anaesthesia and treatment of chronic pain. Hearing loss during or after epidural anesthesia is rare, and it is known to occur by the change of the intracranial pressure. Cerebrospinal fluid is connected with perilymph in the cochlear and vestibule that is important to hearing and balance. If the intracranial pressure is abruptly transferred to the inner ear, perilymph can be leak, that called perilymphatic fistula, dizziness, and hearing loss can occur suddenly. We report a 65-year-old woman who presented with acute onset dizziness and hearing loss during the epidural nerve block for back pain, wherein we speculated a possibility of perilymphatic fistula as the mechanism of hearing loss and dizziness. The mechanism of dizziness and hearing loss was suspected with perilymphatic fistula.
서 론
증 례
고 찰
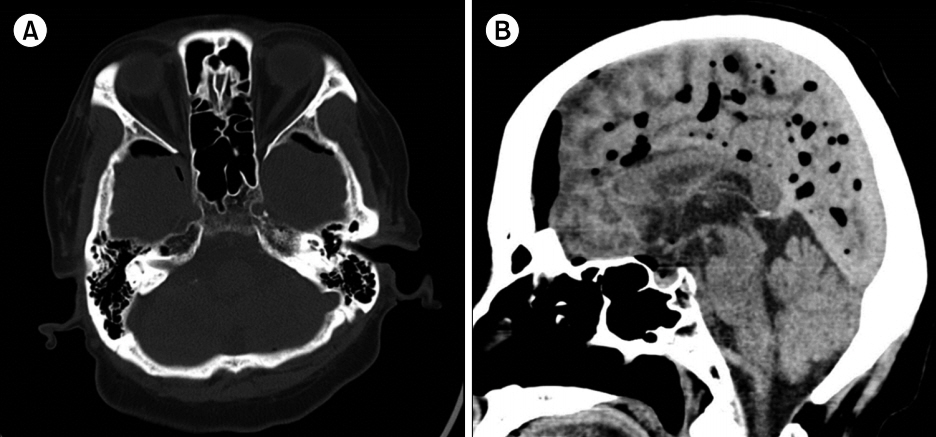
Fig. 1.Brain computed tomographic image. Diffuse pneumocephalus. Axial view (A) and sagittal view (B).
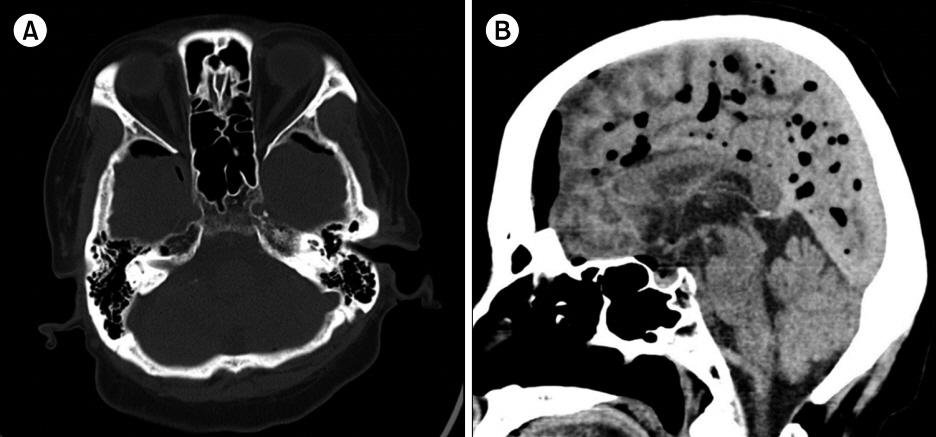

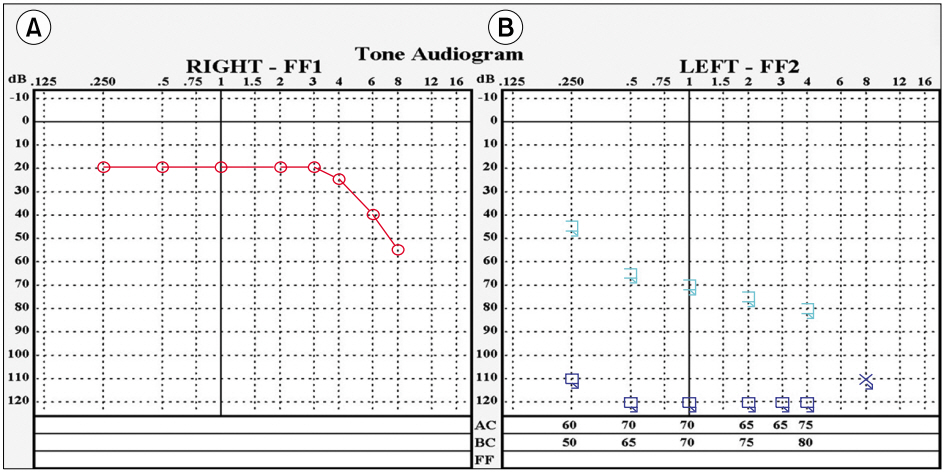
Fig. 2.Pure tone audiogram after hearing loss. Hearing threshold was 20 dB at right side (A) and no response at left side (B).
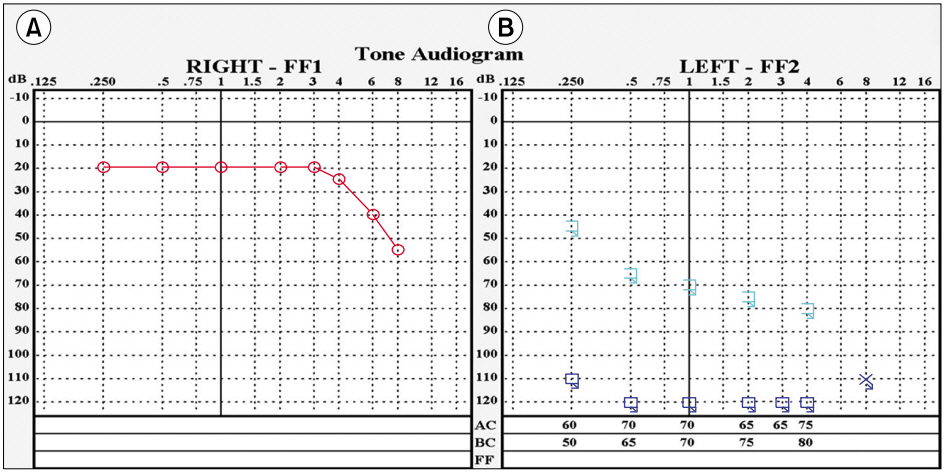

Fig. 3.Caloric test in vestibular function test. Left caloric response was 33% weaker than right. SCV, slow component velocity; avg, average; FI, fixation index; F, Fixation; NF, nonfixation.
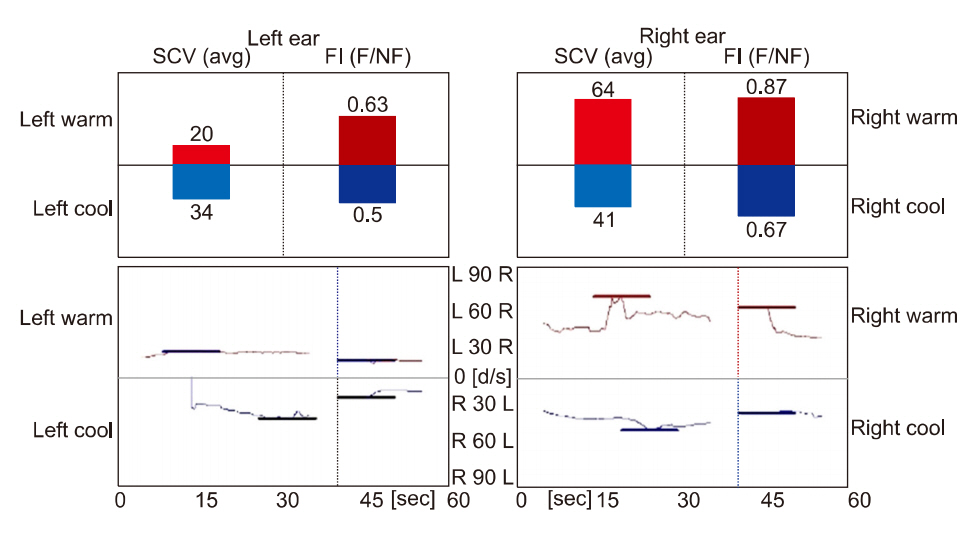

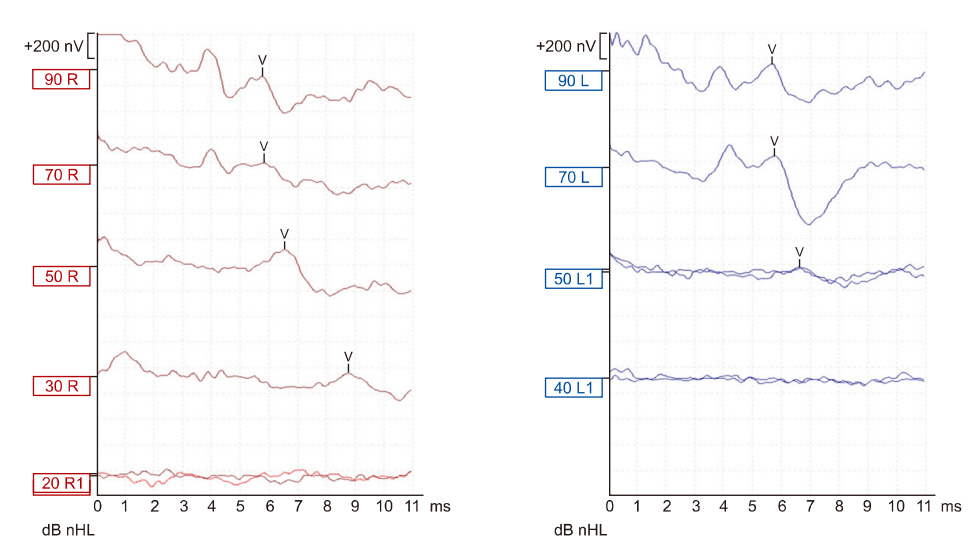
Fig. 4.Auditory brainstem response after treatment. Hearing threshold was 50 dB at left side. nHL, normalized hearing level.


- 1. Auroy Y, Narchi P, Messiah A, Litt L, Rouvier B, Samii K. Serious complications related to regional anesthesia: results of a prospective survey in France. Anesthesiology 1997;87:479–86.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Kiliçkan L, Gürkan Y, Ozkarakas H. Permanent sensorineural hearing loss following spinal anesthesia. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2002;46:1155–7.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Sundberg A, Wang LP, Fog J. Influence of hearing of 22 G Whitacre and 22 G Quincke needles. Anaesthesia 1992;47:981–3.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Stoeckli SJ, Böhmer A. Persistent bilateral hearing loss after shunt placement for hydrocephalus. Case report. J Neurosurg 1999;90:773–5.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Wang LP, Fog J, Bove M. Transient hearing loss following spinal anaesthesia. Anaesthesia 1987;42:1258–63.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Saberski LR, Kondamuri S, Osinubi OY. Identification of the epidural space: is loss of resistance to air a safe technique? A review of the complications related to the use of air. Reg Anesth 1997;22:3–15.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Ciuman RR. Communication routes between intracranial spaces and inner ear: function, pathophysiologic importance and relations with inner ear diseases. Am J Otolaryngol 2009;30:193–202.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Conde M, Villanueva A, Sánchez P, Pérez JA, Ruiz-Rico R. Deafness secondary to lumbar puncture. Rev Neurol 1997;25:1218–20.PubMed
- 9. Goodhill V. Sudden deafness and round window rupture. Laryngoscope 1971;81:1462–74.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Al Felasi M, Pierre G, Mondain M, Uziel A, Venail F. Perilymphatic fistula of the round window. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis 2011;128:139–41.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Cosar A, Yetiser S, Sizlan A, Yanarates O, Yildirim A. Hearing impairment associated with spinal anesthesia. Acta Otolaryngol 2004;124:1159–64.ArticlePubMed
- 12. Truesdale CM, Peterson RB, Hudgins PA, Vivas EX. Internal auditory canal meningocele-perilabyrinthine/translabyrinthine fistula: case report and imaging. Laryngoscope 2016;126:1931–4.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Kohut RI, Hinojosa R, Ryu JH. Update on idiopathic perilymphatic fistulas. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 1996;29:343–52.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Figure
- We recommend
- Related articles
-
- A case of sensorineural hearing loss and vertigo during epidural nerve block
- Vestibular Function and Prognosis of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss with Vertigo
- Vestibular function and Prognosis of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing loss with Vertigo
- Acute Sensorineural Hearing Loss and Tinnitus with Aspirin: A Case Report
- Acute Low Tone Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Consideration for Progression to Meniere’s Disease

 KBS
KBS
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite